6,500+ organizations trust Netchex
Payroll. You know it is important. People have to get paid, right? You know it is complex. But do you really understand all that it encompasses? How much time it takes? The attention to detail?
The short answer is A LOT for all of the above. Payroll is a major, time-consuming process that is integral to your business. Payroll requires a major commitment and investment. It is well worth the time and money needed to make it work properly. You can’t afford to short-change your payroll.
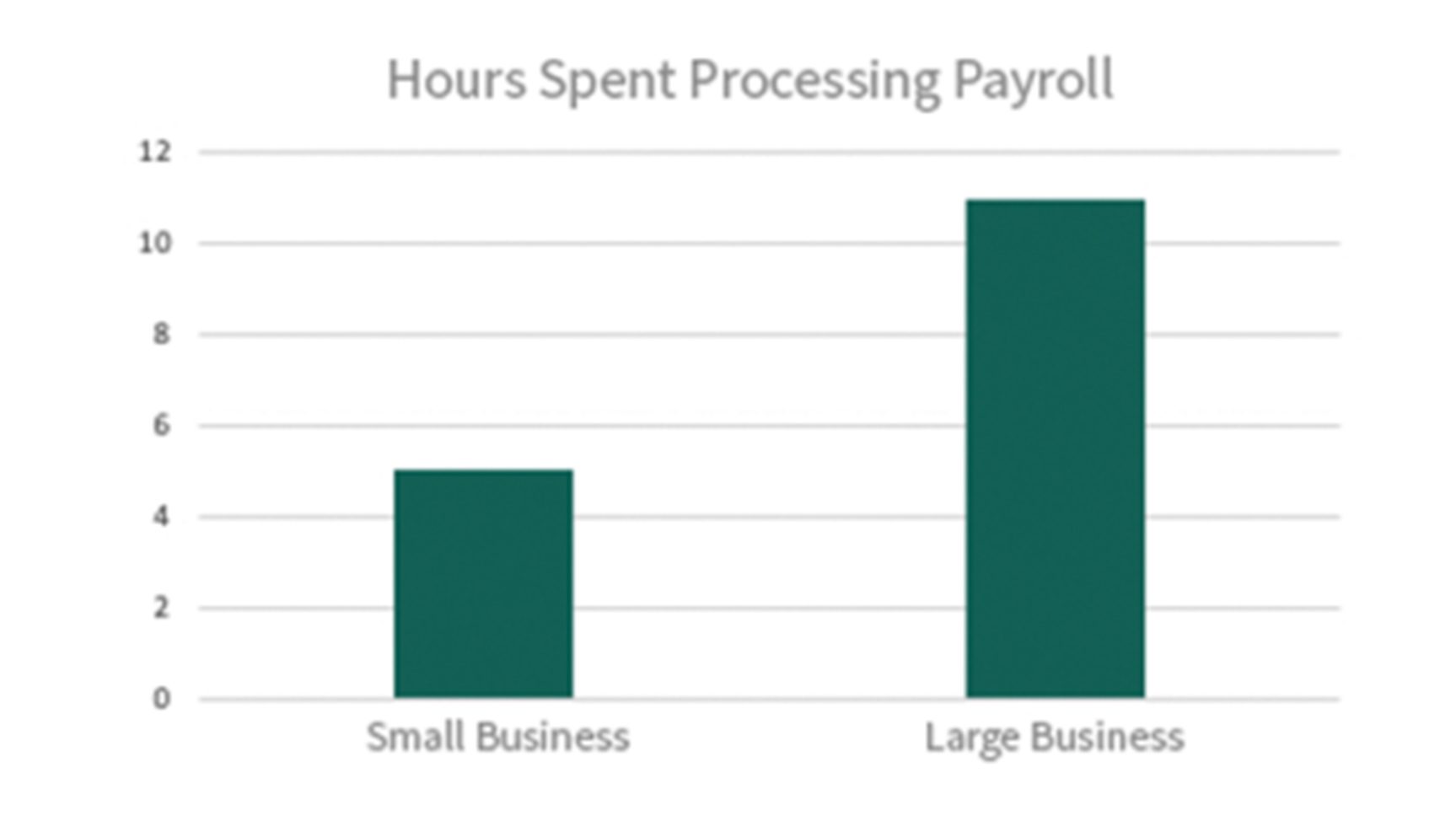
Small Business
owners spend almost 5 hours processing payroll each pay period, whereas larger businesses can spend up to 11 hours
(source: https://smallbiztrends.com)
Companies that do not put the proper resources into it are jeopardizing their business’ financial well-being, as well as that of their employees. No matter how you justify it, adequate payroll processing is a business need, not a want.
But you know that already—that’s why you are here.
What does it take to make payroll work for you—and I mean really work? The best solution is a significant investment in your company and your employees through payroll software.
Payroll software significantly eases the workload for your company, while also promoting stability, consistency, and peace of mind—leaving you more time for you to focus on running your business. It is a commitment to getting things done right and on time—the two things that are now more important than ever.
The Importance of Payroll
Payroll is perhaps the most important financial component of any business. Not only does it encompass the most obvious—employees being paid—it also goes a long way in determining the overall net profit of a company. On top of that, payroll is rightfully subjected to numerous laws, regulations, and ethical considerations. To say the least, it requires a lot of time and attention.
First off, businesses are legally obligated to pay their employees timely and accurately. When a company hires an employee, each party enters into an agreement centered on payment for labor combined with an employee benefits package.
Ensuring this happens, the U.S. Department of Labor is responsible for the enforcement of everything pay-related—from minimum wage and overtime requirements to deductions and employee classifications.
When a business fails to comply with any of these laws, employers are held accountable for things like back wages, penalties, attorney fees, and may even face criminal or civil penalties.
Additionally, businesses are required by federal and state governments to withhold a percentage of each paycheck, including Social Security, Medicare, unemployment, and income tax on the Federal level, as well as state income taxes, unemployment, and disability taxes. Failure to properly manage these taxes can result in severe financial penalties, a tax audit, and even tax liens.
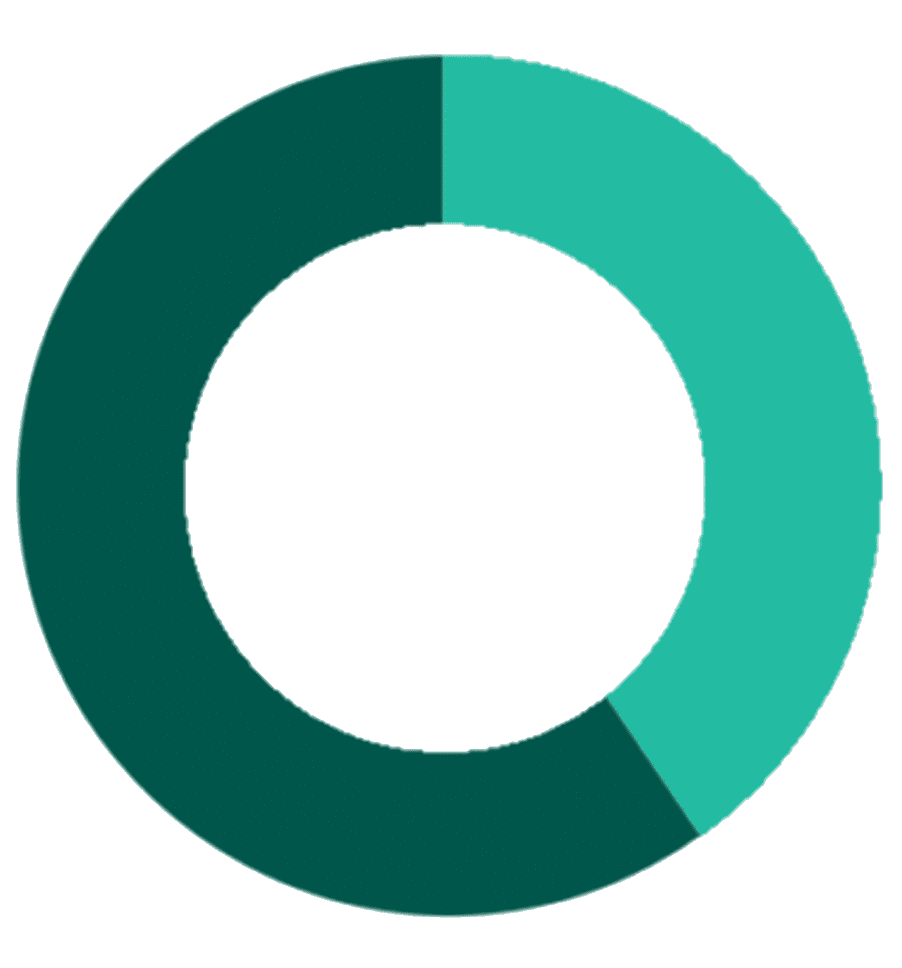
40%
of small businesses incur an average of $845 each year in penalties for late or incorrect filings or payments
source: https://www.accountingtoday.com)
And finally, beyond employee pay and tax considerations, payroll offers unique, detailed financial insight into your company. An accurate payroll is the first step in determining whether or not a business is turning a profit and how it can grow.
Should you hire new employees? Can you afford to hire new employees? Accurate payroll data can help your business answer these questions and more.
Experience the Netchex advantage: advanced technology & unrivaled customer support.
How Payroll Works
And finally, beyond employee pay and tax considerations, payroll offers unique, detailed financial insight into your company. An accurate payroll is the first step in determining whether or not a business is turning a profit and how it can grow.
Should you hire new employees? Can you afford to hire new employees? Accurate payroll data can help your business answer these questions and more.
Starting a new payroll or switching payroll providers can seem like a daunting task. Although the payroll process is largely standardized across the board, it is a very time-consuming and detailed process and may differ slightly based on what payroll software you use.
Payroll touches multiple parts of the business, including finance. But for the most part, payroll is an HR process and typically run by an HR professional or Payroll Specialist.
Who runs payroll
The majority of payroll data originates from HR activities, such as recruiting and onboarding (new hires) and performance management (raises and bonuses). Additionally, privacy—a crucial element of all things HR—is also important. So, it makes sense that HR would lead the charge when it comes to payroll as well.
But by learning the intricacies of the payroll process and all that is involved, business leaders can also gain a better understanding of the financial health of their organization, as well as a better appreciation for the administrators performing one of the most essential, time-consuming, and stressful tasks.
Discover what information and documentation you need, as well as the decision that must be made, in order to successfully run a payroll.
Transform your HR operations with Netchex’s innovative technology & unparalleled customer service.
What you need to process payroll
Prior to running your first payroll, you will need to gather the following information:
EIN (Employer Identification Number)
The unique number the federal government uses to identify an organization for tax purposes. This nine-digit number is needed to pay federal taxes, hire employees, open bank accounts, and apply for business licenses and permits. Applying for an EIN is free of charge and processed through the IRS.
State and local ID numbers
Serves the same function as your EIN, but at the state and local level.
Employee Personal Information
Pertinent personal information, such as full legal name, current address, and social security number, must be gathered of all employees in order to process payroll.
Employee tax information
W-4 forms for full and part-time employees and W-9s for contract employees are needed. This information can be collected from new hires during the onboarding process.
Previous payroll records
Maintaining previous payroll records makes switching payroll providers easier and more efficient. Adding payroll history into your new payroll software facilitates more accurately calculated taxes and deductions, as well more detailed and useful payroll data and reporting.
Understanding worker classifications & compensation
Since each group comes with its own set of rules and requirements it is important to classify all employees correctly and how payments will be set up.
Employee vs. independent contractor
Worker classification is critical because it determines if an employer must withhold income taxes and pay Social Security, Medicare taxes, and unemployment tax. Businesses do not have to withhold or pay any taxes with independent contractors, but are required to do so for employees.
Exempt vs. non-exempt employees
According to the IRS, there are three factors employers must use to determine classification: behavioral control, financial control, and relationship. Misclassification of an employee leads to direct consequences, including making employers liable for employment taxes.
An employee’s status is determined by three important factors: salary vs. hourly, salary amount, and expected job duties.
Exempt employees are exempt from overtime and minimum wage rules. Qualifications for exempt status are:
- The employee must earn a salary of $35,568 per year ($684 per week).
- The employee must have executive, administrative, or professional job duties.
Non-exempt employees can be salaried, but are typically hourly. These employees are not exempt from FLSA overtime and minimum wage rules. This status means that companies must pay non-exempt employees overtime wages whenever they work overtime hours.
How to process payroll
Decide how you want to pay your employees
Employees today expect options to be available to them in every aspect of the workplace, including payday. Paper checks and direct deposit are still the norm, but new methods, such as payroll cards, have emerged for an evolving workforce.
Determine when you want to pay your employees
A payroll schedule, or pay frequency, is how often you will pay your employees—weekly, bi-monthly, monthly. The decision is ultimately your’s to make, but some states regulate which pay periods can be used.
Additionally, this schedule establishes employee pay dates, tax payment due dates, and tax return filing deadlines. Scheduling for special payrolls, such as for seasonal or annual bonuses, should be decided upfront as well.
Track employee time and attendance
Accurate payroll is dependent on accurate employee time tracking. Though like payroll itself, time and attendance can be tracked manually, it is far more time consuming and prone to errors.
A time and attendance solution that is directly integrated with payroll software offers the easiest and most seamless option for your business.
Differentiate types of pay
- Gross pay is the amount that employees receive before deductions.
- Net pay is the amount an employee takes home after deductions.
- Bonus pay is additional compensation provided to an employee. Both cash and non-cash bonuses are subject to income tax withholding and payroll taxes.
Factor in overtime pay
Whenever a non-exempt employee works more than 40 hours in a single workweek, they are eligible for overtime.
The easiest way to determine overtime pay is 50% more than an employee’s regular rate for all overtime hours, also known as “time and a half.” If there are no additional payments, such as non-discretionary bonuses or commissions, multiply the employee’s regular hourly rate by 1.5 and apply that expanded rate to only the overtime hours worked.
Wage garnishments
A wage garnishment is any legally-binding order that an employer must withhold a specific portion of an employee’s paycheck to be sent to whomever an employee owes money. Garnishments can be used for the payment of a debt such as alimony, child support, student loan default, or other circumstances until that debt is resolved.
Once informed of the required garnishment, employers must alert the employee and immediately begin the wage garnishment process by ensuring payments are sent to the correct agency or creditor. Employers are obligated to factor these into their payroll process or face legal repercussions for failing to honor the court order.
Employee benefits contributions
A major component of payroll is employee benefits management. This accounts for all benefits contributions from each individual employee, including work-sponsored retirement plans, health insurance (including dental and vision), life insurance, flexible spending accounts, and more.
When processing payroll, businesses need to calculate and deduct each employee’s individual benefits contributions from each paycheck. Any miscalculations or late payments could result in a lapse in coverage for your employees and serious legal consequences for your business.
Factoring in payroll taxes & compliance
Employers have to withhold federal and state income tax from all employees’ taxable wages, based on what employees include on their Form W-4.
Employers have several mandatory tasks in handling payroll taxes:
- Figure income tax withholding and other employment taxes.
- Deposit all employment taxes according to a set deposit schedule.
- Report quarterly about their employment taxes covering income tax withholding and FICA.
- Report annually to employees and the Social Security Administration about employee’s tax payments.
- FUTA (Federal Unemployment Tax Act) and other state-level reporting.
Finding a payroll software that takes care of payroll taxes for you is ideal. First, you will need to give them access to your tax information, including your tax filing identification numbers. Your payroll provider also needs to know your depositing schedule for federal income and FICA taxes. You also need to authorize the company to handle taxes for you by filling out Form 8655.
Benefits of Outsourcing Payroll
So, as you can see, payroll is a monumental task. If you are still doing payroll in-house, you are severely limiting your company’s potential. Outsourcing payroll and other back office functions offer numerous benefits across your company from day one.
Save time with greater productivity
Through improved processes and automation, the right payroll software can significantly cut down on the time it takes to process payroll each pay period. This allows business leaders, managers, and HR to spend their time on actually running the business and focused on helping employees.
Reduce costs with increased accuracy
Manually processing payroll is likely costing your company revenue. Whether underpaying or overpaying, payroll errors result in IRS penalties and waste countless hours correcting. Eliminate this wasted time and money with an accurate payroll software system.
Improve compliance with help from industry experts
Partnering with a trusted payroll software company greatly reduces the burden on businesses to remain up-to-date and compliant with the numerous and constantly changing laws and legislation. With tax compliance experts on staff to ensure compliance, payroll companies like Netchex keep your company safe and worry-free.
Enhance security and privacy
The information gathered by HR for processing payroll demands privacy—ethically and legally. Working with in-house processes or multiple, disconnected systems leaves your business vulnerable to security threats and privacy leaks. An investment in payroll software is a commitment to the security of your company’s sensitive information.
Empower employees
Self-service functionality helps engage and empower employees by giving them access to everything they need to manage their workplace experience. Personalized (and mobile) self-service allows employees to access their own records, make changes, request PTO, and answer their own questions before contacting a manager or HR.
Grow your business with better data and analytics
Collecting and analyzing data over time improves your processes and overall business by identifying goals and tracking progress over time. Gain easy, instant access to reporting that you regularly need like instant payroll preview, payment errors, time & attendance updates, payroll processing time spent, and up-to-the-minute compliance standards.
Gateway to HR technology
Payroll is the key to a truly integrated HR technology system. A lot goes into payroll, and the right payroll software can cover and connect it all—including time and attendance, benefits administration, performance management, learning management, recruiting, onboarding, and more.
