Understanding to Payroll Management
Payroll is perhaps the most important financial component of any business. Not only does it encompass the most obvious—employees being paid—it also goes a long way in determining the overall net profit of a company. On top of that, payroll is rightfully subjected to numerous laws, regulations, and ethical considerations. To say the least, it requires a lot of time and attention.
First off, businesses are legally obligated to pay their employees timely and accurately. When a company hires an employee, each party enters into an agreement centered on payment for labor combined with an employee benefits package.
Ensuring this happens, the U.S. Department of Labor is responsible for the enforcement of everything pay-related—from minimum wage and overtime requirements to deductions and employee classifications.
When a business fails to comply with any of these laws, employers are held accountable for things like back wages, penalties, attorney fees, and may even face criminal or civil penalties.
Additionally, businesses are required by federal and state governments to withhold a percentage of each paycheck, including Social Security, Medicare, unemployment, and income tax on the Federal level, as well as state income taxes, unemployment, and disability taxes. Failure to properly manage these taxes can result in severe financial penalties, a tax audit, and even tax liens.
And finally, beyond employee pay and tax considerations, payroll offers unique, detailed financial insight into your company. An accurate payroll is the first step in determining whether or not a business is turning a profit and how it can grow.
Key Takeaways:
- Payroll is a complicated and multifaceted workstream that requires expertise and diligence
- Bad payroll administration is a surefire way to lose employees and open your company to legal and financial consequences
- The right software solution will streamline payroll processing and reduce the administrative burden
- Improved compliance with labor laws and regulations ensures that payments are accurate and timely
Should you hire new employees? Can you afford to hire new employees? Accurate payroll data can help your business answer these questions and more.
Processing Payroll
There are a number of considerations off the top that have to be decided before beginning payroll:
- Payment methods
- Payment Frequency
- Tracking time and attendance
- Different types of pay
- Overtime pay
- Wage garnishments
- Benefits contributions
Let’s look at each:
What are the necessary features of payroll processing software?
While specific features can vary based on both user and provider, payroll technology should include most (if not all) of these essential functions.
Accurately calculate wages earned for each employee
Integrate seamlessly with time & attendance and other HR technology solutions
Withhold taxes and other deductions from paychecks
Deposit tax payments to the appropriate recipient on-time
Pay employees accurately and on-time
Enable beneficial payroll reports
Facilitate easier new employee onboarding
Protect sensitive employee data and financial information
Empower employees with self-service functionality
Decide how you want to pay your employees
Employees today expect options to be available to them in every aspect of the workplace, including payday. Paper checks and direct deposit are still the norm, but new methods, such as payroll cards, have emerged for an evolving workforce.
Payroll Frequency: Determine when you want to pay your employees
More Than Just A Paycheck
There’s more than one way to pay. Today’s workforce can be remote, seasonal, part-time, or salaried. And Netchex can be just as varied depending on your needs.
- NetDirect unlimited direct deposit
- Live checks through our NetPay system
- Paycards with the Skylight® PayOptions™ Program from Netspend®
A payroll schedule, or pay frequency, is how often you will pay your employees—weekly, bi-monthly, monthly. The decision is ultimately yours to make, but some states regulate which pay periods can be used.
Additionally, this schedule establishes employee pay dates, tax payment due dates, and tax return filing deadlines. Scheduling for special payrolls, such as seasonal or annual bonuses, should also be decided upfront.
Earned Wage Access
A unique and beneficial financial service, Earned Wage Access (EWA) enables employees to voluntarily access their earned wages before your company’s scheduled payday frequency (usually weekly, bi-weekly, or monthly).
- Employees can collect a portion of their earned wages at any time during the pay period
- EWA is designed to provide workers with more flexibility and control over their finances.
How Earned Wage Access Works
Earned Wage Access doesn’t have to be complicated. Through our integration with Rain, EWA is easy to use and collects limited data, offering a safe and efficient way to deliver earned wages to employees.
Sign Up
Enroll in Netchex’s Earned Wage Access feature through their employer’s payroll system. It’s quick and easy to get started. Simply provide your information, set up your account, and gain access to the benefits of Earned Wage Access.
Request Funds
Whenever you need access to your earned wages, simply log in to your Netchex account and request the amount you need. You can choose to receive the funds instantly or on your next payday, depending on your preference and urgency.
Get Your Money
Once your request is approved, your funds will be deposited directly into your bank account. No waiting, no hassle. You can access your money whenever you need it, giving you the financial flexibility you deserve.
Track & Manage
Keep track of your earned wages and manage your requests through the Netchex platform. It’s transparent, convenient, and puts you in control. You can easily view your transaction history, monitor your available balance, and make future requests as needed.
Track employee time and attendance
Accurate payroll is dependent on accurate employee time tracking. Though like payroll itself, time and attendance can be tracked manually, it is far more time-consuming and prone to errors.
A time and attendance solution that is directly integrated with payroll software offers the easiest and most seamless option for your business.
Differentiate types of pay
Employers need to understand different types of pay and when they should be used for the best accuracy and compliance.
Tax and Compliance
Get tasks off your plate and worries off your mind. Automated taxes and reporting to help ensure accuracy—one less thing to think about, thanks to Netchex payroll software.
Our Address, Compensation, and Tax Verification (ACT) feature helps you ensure your employees are being taxed accordingly and paid the appropriate minimum wage based on their location.
Automation & Reporting
- Electronic IRS filing and pay withdrawals
- Automate reporting and data pulls
- Quarterly online tax statements & W2 preview
- New hire reporting
- Gross pay is the amount that employees receive before deductions.
- Net pay is the amount an employee takes home after deductions.
- Bonus pay is additional compensation provided to an employee. Both cash and non-cash bonuses are subject to income tax withholding and payroll taxes.
Factor in overtime pay
Whenever a non-exempt employee works more than 40 hours in a single workweek, they are eligible for overtime.
The easiest way to determine overtime pay is 50% more than an employee’s regular rate for all overtime hours, also known as “time and a half.” If there are no additional payments, such as non-discretionary bonuses or commissions, multiply the employee’s regular hourly rate by 1.5 and apply that expanded rate to only the overtime hours worked.
Wage garnishments
A wage garnishment is any legally binding order that an employer must withhold a specific portion of an employee’s paycheck to be sent to whomever an employee owes money. Garnishments can be used for the payment of a debt such as alimony, child support, student loan default, or other circumstances until that debt is resolved.
Once informed of the required garnishment, employers must alert the employee and immediately begin the wage garnishment process by ensuring payments are sent to the correct agency or creditor. Employers are obligated to factor these into their payroll process or face legal repercussions for failing to honor the court order.
Employee benefits contributions
A major component of payroll is employee benefits management. This accounts for all benefits contributions from each individual employee, including work-sponsored retirement plans, health insurance (including dental and vision), life insurance, flexible spending accounts, and more.
When processing payroll, businesses need to calculate and deduct each employee’s individual benefits contributions from each paycheck. Any miscalculations or late payments could result in a lapse in coverage for your employees and serious legal consequences for your business.
In-house vs Outsourced Payroll
All businesses must consider how to handle payroll processing. Small business owners might be able to manage payroll themselves, but it takes time and is susceptible to errors.
Medium and large businesses can justify hiring a dedicated HR professional, but time, errors, and cost are still less than ideal.
Outsourcing Payroll

Anyone can run payroll

Quick and efficient

Easy and streamlined

Full integration

Safe and secure data

Automated taxes

Service team of experts

Built-in reporting & analytics

Accurate and error-free

Supports compliance
In-House Payroll

Requires dedicated employee

Time consuming for all

Complicated process

Subject to errors

No integration w/ HR functions

Lack of security

Tax complications

Lack of expertise

Cost savings

Manual reporting
The right software solution can make payroll tasks faster and easier for all size businesses.
How should your company be processing payroll?
Read about the considerations of doing payroll in-house vs outsourcing your payroll.
What you need to process payroll
Whether you are doing it yourself or outsourcing it, prior to running your first payroll, you will need to gather the following information:
EIN (Employer Identification Number)
The unique number the federal government uses to identify an organization for tax purposes. This nine-digit number is needed to pay federal taxes, hire employees, open bank accounts, and apply for business licenses and permits. Applying for an EIN is free of charge and processed through the IRS.
State and local ID numbers
Serves the same function as your EIN, but at the state and local level.
Employee Personal Information
Pertinent personal information, such as full legal name, current address, and social security number, must be gathered of all employees in order to process payroll.
Employee tax information
W-4 forms for full and part-time employees and W-9s for contract employees are needed. This information can be collected from new hires during the onboarding process.
Previous payroll records
Maintaining previous payroll records makes switching payroll providers easier and more efficient. Adding payroll history into your new payroll software facilitates more accurately calculated taxes and deductions, as well more detailed and useful payroll data and reporting.
Understanding worker classifications
It is important to classify all employees correctly and determine how payments will be set up since each group has its own set of rules and requirements.
Employee vs. independent contractor
Worker classification is critical because it determines if an employer must withhold income taxes and pay Social Security, Medicare taxes, and unemployment tax. Businesses do not have to withhold or pay any taxes with independent contractors, but are required to do so for employees.
Exempt vs. non-exempt employees
According to the IRS, there are three factors employers must use to determine classification: behavioral control, financial control, and relationship. Misclassification of an employee leads to direct consequences, including making employers liable for employment taxes.
An employee’s status is determined by three important factors: salary vs. hourly, salary amount, and expected job duties.
Exempt employees are exempt from overtime and minimum wage rules. Qualifications for exempt status are:
- The employee must earn a salary of $35,568 per year ($684 per week).
- The employee must have executive, administrative, or professional job duties.
Non-exempt employees can be salaried, but are typically hourly. These employees are not exempt from FLSA overtime and minimum wage rules. This status means that companies must pay non-exempt employees overtime wages whenever they work overtime hours.
Payroll for Different Business Types
Small Business Payroll
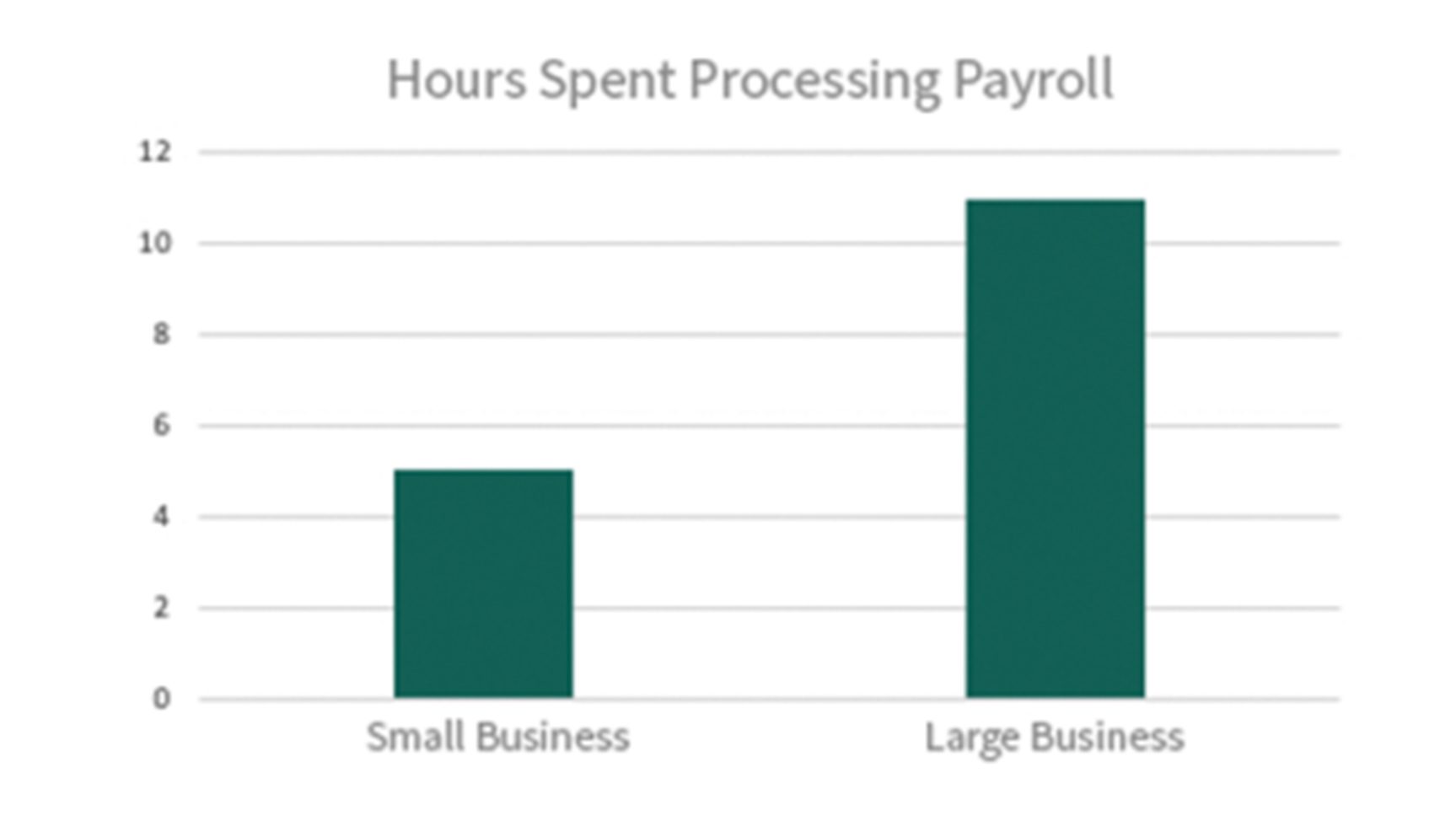
Small Business
owners spend almost 5 hours processing payroll each pay period, whereas larger businesses can spend up to 11 hours
(source: https://smallbiztrends.com)
Running a small business is hard—there’s no doubt about it. There are a million things to consider, plan, and execute daily. And by its very nature, armed only with a limited staff to do all of it.
Because of this, many small businesses spread themselves too thin, especially when it comes to back office functions. Others lack the HR expertise to understand all of what they are short-changing. Regardless of the circumstances, countless small businesses are hindering themselves in terms of efficiency and growth.
Small businesses need all the help they can get to survive and succeed.
Learn more about payroll management for small business.
Large Business Payroll
For a large business, payroll administration typically means more work. A greater number of employees equates to more time and effort throughout the payroll process to ensure accuracy and timeliness.
Simplify HR management and payroll processing with Netchex’s powerful payroll software for large companies. Built for large businesses, Netchex payroll software is a comprehensive suite of HR tech designed to let you work more efficiently.
Netchex’s single sign-on payroll and HR software lets you streamline and automate much of the manual work associated with payroll administration. For companies with 250+ employees, this frees up valuable HR time to focus more on initiatives, goals, and most importantly, your people.
Learn more about how Netchex can help large businesses with HR, payroll, and more.
Multi-location and franchises
When managing a franchise, each location must be fully staffed and scheduled, policies and training need to be consistent, and employee data and comparison reporting must be available. Learn more about payroll and HR considerations for multiple locations and franchises.
Common Payroll Challenges
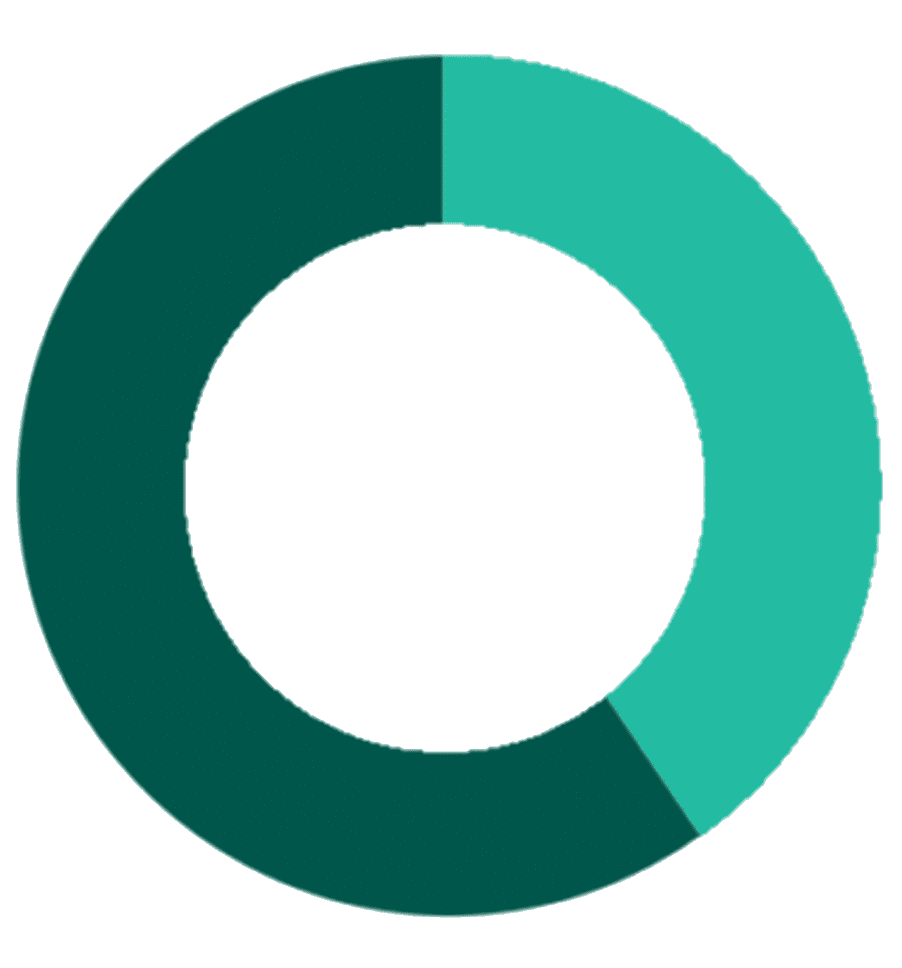
40%
of small businesses incur an average of $845 each year in penalties for late or incorrect filings or payments
source: https://www.accountingtoday.com
Companies that do not put the proper resources into it are jeopardizing their business’ financial well-being, as well as that of their employees. No matter how you justify it, adequate payroll processing is a business need, not a want.
Payroll errors can have disastrous, cascading consequences for any business, especially smaller ones who can’t afford lost revenue, let alone fines and penalties that might add up.
Always be careful to avoid payroll scams, such as phishing.
But you know that already—that’s why you are here.
What does it take to make payroll work for you—and I mean really work? The best solution is a significant investment in your company and your employees through payroll software.
Payroll software significantly eases the workload for your company, while also promoting stability, consistency, and peace of mind—leaving you more time for you to focus on running your business. It is a commitment to getting things done right and on time—the two things that are now more important than ever.
Benefits of Payroll Management
Assists with payroll accuracy
Payroll errors can be costly, compliance isn’t optional, and underpaid employees will revolt. Software makes the payroll process consistent and precise.
Enables on-time payments
Just as important as accuracy, timeliness of payments is critical. Employees depend on their paychecks to be available on the expected day.
Offers multiple payday options
Employees want more options than just paper checks and direct deposit. Payroll cards are a burgeoning alternative and another step towards a cashless world.
Simplifies taxes
Invest in a robust payroll processing software solution that you can trust to handle local, state, and federal taxes. Calculations and routine payments should be automatic.
Secures personal data
Data security is no joke. Payroll data includes sensitive personal and financial information, which your employees need to know is safe.
Integrates easily with other HR software
Payroll should be the gateway to all other HR software solutions—from timekeeping and benefits to onboarding and performanc
Increases employee engagement and productivity
Online payroll software enables employees to actively participate in the HR process. This typically includes:
- 24/7 access to pay stubs
- Tax forms
Payroll Software/Systems and Technology
Payroll software is the foundation of any operating business. Used to manage, organize, and automate employee payments, it tracks all the criteria needed to make payments and maintains the necessary payment data.
Payroll software encourages consistency, ensures accuracy, and gives business owners peace of mind that their company and employees are financially secure.
Learn more about why your business needs to invest in payroll software.
Gateway to HR technology
(Most Valuable Payroll) for Your Business
Netchex is a true team player providing access, information, and cross-functionality to every department in your company.Our Address, Compensation, and Tax Verification (ACT) feature helps you ensure your employees are being taxed accordingly and paid the appropriate minimum wage based on their location.
- Time & Attendance integration
- Benefits Administration integration
- Cross-company reporting for labor cost analysis
- Employee self-service PTO requests and real-time accruals
Payroll is the key to a truly integrated HR technology system. A lot goes into payroll, and the right payroll software can cover and connect it all—including time and attendance, benefits administration, performance management, learning management, recruiting, onboarding, and more.
Payroll Security
A solid security program will have documented policies and procedures, business continuity plan, a disaster recovery plan, and an incident response plan in place. This is difficult for a small business.
At the same time, it is understandable that many businesses are nervous about allowing a third party to handle payroll and other HR processes. With a few simple steps, you can perform your own due diligence to determine whether they are a reliable company and up to the task of meeting your needs.
Learn more about finding a trustworthy payroll company.
Why Netchex
Streamline Payroll Management with Netchex
Netchex offers comprehensive payroll solutions designed to simplify and optimize your payroll processes. Why we stand out:
User-Friendly Payroll Software: Our platform is easy to use, including for new users. This reduces errors and reduces the need for lengthy onboarding sessions, saving valuable time.
Integrated HR Technology: Payroll management is just the gateway to a fully integrated HR system, seamlessly connecting payroll with time and attendance tracking, benefits administration, recruiting, onboarding, and more.
Enhanced Compliance: Stay in-the-know on all of the latest labor laws and regulations. Netchex helps you navigate the complexities of tax filings, wage garnishments, and employee classifications, minimizing the risk of costly penalties.
Superior Customer Support: Our dedicated team of experts is always ready to assist you, ensuring that your payroll processes can continue uninterrupted.
Robust Security Measures: Data security is a top priority here at Netchex. Keep sensitive employee data safe with advanced security protocols, protecting you and your company in an era where payroll scams and data breaches are rampant.
Take the Next Step with Netchex
Ready to transform your payroll process and reduce administrative workloads?
Discover what Netchex can do for you.
Request a Quote today and take the first step toward a more efficient, compliant, and stress-free payroll system.
This article is part of our comprehensive payroll management series.
